With the deadline approaching, organizations and businesses dependent on Aadhaar-based authentication services have to gear up for a major change in the adopted technology. UIDAI has directed the shift from L0 RD (Registered Device) fingerprint readers to L1 RD fingerprint readers. This is aimed at enhancing the accuracy, efficiency, and security of Aadhaar-authenticated authentication like the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AEPS), eKYC, and biometric attendance systems.
The following is this blog discussing why this change matters, the main differences between L0 and L1 devices, the benefits of L1 scanners, and how it may affect various industries. It will also discuss the challenges companies encounter while transitioning to L1 RD devices and offer a step-by-step guide for a smooth transition. With the deadline approaching, it is imperative that all biometric device holders get ready for the new technology to provide seamless and secure Aadhaar authentication.
Why is UIDAI Transitioning from L0 to L1 RD Devices?
L0 RD fingerprint scanners have been the bread and butter of Aadhaar-based biometric authentication for several years. L0 devices, primarily based on optical sensors, have enabled millions of identifications and transactions. L0 devices incorporate vulnerabilities that inactivate their functionality and security, although.
Limitations of L0 Devices:
-
High False Rejection Rates: L0 sensors are not very accurate and detect the overall patterns of the fingerprint but not the minute details. This leads to high false rejection rates, especially among individuals with hard fingerprints (e.g., the elderly or those who have developed worn-out fingerprints with time).
-
Slower Processing Speed: L0 devices have slower processing speed and therefore lag occurs during high-density usage times, especially in locations with heavy use such as government offices, public service entities, and banks.
-
Security Flaws: L0 devices have basic optical sensors and contain highly minimal security characteristics. These scanners are more prone to data exposure and therefore are not a very secure choice for biometric authentication.
Thereby, UIDAI has decided to shift its focus from L0 RD devices to L1 RD devices. L1 devices use capacitive sensors that bring multiple benefits in terms of overhauling the shortcomings of L0 devices.
The Benefits of Transitioning to L1 RD Devices:
-
Higher Accuracy: L1 RD instruments are more accurate in gathering fingerprint data by recognizing ridge endings and pore patterns, and thus more accurate fingerprint data to match.
-
Enhanced Speed of Processing: L1 scanners process biometric information at much higher speeds. This decreases waiting time and provides an improved user experience, even for high-traffic sites.
-
Enhanced Security: L1 devices have enhanced encryption and Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) features, which make the biometric information more secure and less vulnerable to unauthorized access.
-
Versatility: L1 RD fingerprint readers are more lenient in different conditions and function well even with wet, dry, or dirty fingers, a significant enhancement over L0 readers.
These advances make the L1 RD fingerprint scanners an essential component of India's Aadhaar system, delivering a more secure and efficient authentication experience.
Key Differences Between L0 and L1 RD Fingerprint Scanners
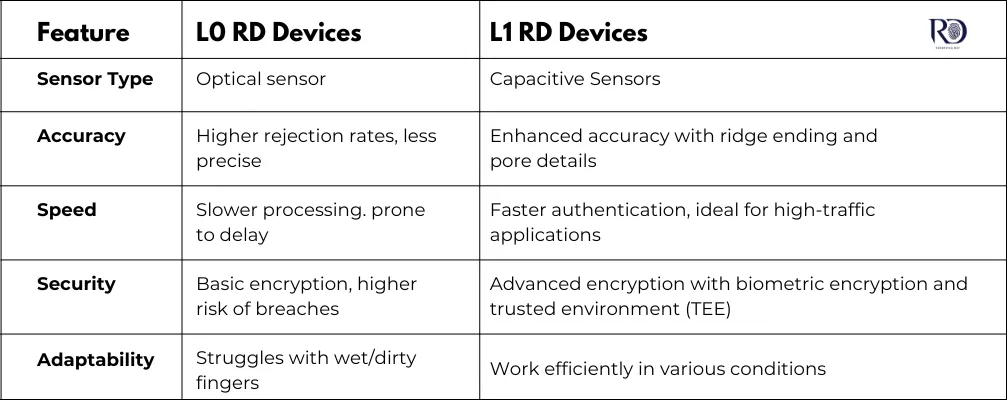
In order to comprehend the shift from L0 to L1 RD devices, one should compare their main characteristics. The main differences between these devices are in their sensor types, precision, speed, security features, and general reliability.
Sensor Technology
The most basic difference between L0 and L1 devices is sensor technology. L0 RD devices use optical sensors, which image the fingerprint pattern by capturing the fingerprint. This approach works, but it has a chance to fail under harsh conditions such as wet or dirty fingers. L1 RD devices, however, use capacitive sensors, which function by sensing the electrical characteristics of the ridges and valleys of the fingerprint. Capacitive sensors provide much greater accuracy, even in adverse environments.
Accuracy and Reliability
L1 RD fingerprint scanners are intended to scan more detailed fingerprint minutiae to provide a more accurate level of detail than L0 devices. Greater accuracy reduces false rejection, which makes the authentication more reliable, particularly for applications like AEPS and biometric attendance. The more precise the scan of the fingerprint, the less number of times an individual will authenticate incorrectly.
Speed of Authentication
Speed of processing is important in heavy-usage applications such as banking and government services. L0 devices, as they are slower, are time-consuming and lead to user discontent. L1 devices, with their faster processing rates, give a much more comfortable experience, especially in instances where large numbers of users have to be authenticated within a limited time.
Security Features
Security is the chief parameter in case of Aadhaar authentication. L0 devices provide simple encryption mechanisms that are easy to breach and misuse. L1 devices have enhanced security functionalities such as biometric encryption and Trusted Execution Environments (TEE). These types of security parameters provide safe storage of sensitive biometric information as well as authentication.
Adaptability
L1 RD fingerprint readers are more adaptive than L0 devices. While L0 scanners cannot authenticate users with wet, dry, or injured fingers, L1 devices are programmed to perform well in most conditions. This functionality makes it possible for users to authenticate themselves suitably in different environments without risking rejection because of challenging fingerprint conditions.
Advantages of L1 RD Fingerprint Scanners
The transition to L1 RD fingerprint scanners brings some welcome benefits that improve the whole user and organizational experience. Among the main advantages are:
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Fewer Rejections
L1 RD fingerprint scanners provide improved accuracy in biometric authentication with less false rejections. This is the most critical aspect when one needs such situations as AEPS transactions, biometric attendance, and delivery of government services, where a failure in authentication causes delay and inconvenience.
2. Increased Processing Speeds
L1 devices are engineered for speed, biometric data processed quickly and with efficiency. They are optimally positioned in high-traffic applications such as shopping malls, government agencies, and banks. With the accelerated authentication, there is enhancement of the end-user experience, and there is minimal delay and bottleneck.
3. Strengthened Security Mechanisms
Security is of highest importance to UIDAI, particularly when it concerns the massive amount of sensitive data that comes into play with Aadhaar transactions. L1 RD fingerprint readers provide enhanced security features such as biometric encryption and Trusted Execution Environment support. They protect the biometrics and make them cyber attack-resistant.
4. Enhanced Performance under Harsh Conditions
L1 devices are also highly effective under different environmental conditions, e.g., with wet, dirty, or battered fingers. This adaptability minimizes the risk of authentication failure, whereby users can easily carry out their transactions without hassle irrespective of the condition of their fingers.
5. Better Efficiency in Financial Services
For the banking and financial institutions, AEPS transactions rely on fingerprint verification. L1 scanners ensure that authentication failures are minimized, allowing customers to make transactions within time. This is especially helpful in rural areas, where the quality of users' fingerprint information is unpredictable.
Impact of Aadhaar Authentication on Different Sectors
1. Banking and Financial Services
The financial industry, with vital stakes in Aadhaar authentication, will greatly gain by switching to L1 devices. L1 scanners will ensure higher security and performance along with lower transaction failure and fewer fraud transactions. Improved processing times in high-priority banking applications will lead to greater customer satisfaction and process automation.
2. Government Welfare Schemes
The Aadhaar authentication is reliant upon most government schemes such as direct benefit transfer (DBT), pension schemes, and ration supply. The migration to L1 RD device will phase out fraud claims while the benefits reach the respective beneficiaries. The higher precision and speed of L1 scanners will also ensure easier service delivery to beneficiaries at the risk of authentication failure.
3. Corporate and Workforce Management
For companies using biometric attendance systems, the transition to L1 devices will further automate the employees' identification process. This will decrease failed login due to low-quality fingerprints, amounting to simpler workforce management and payroll processing.
4. Healthcare and Insurance
Hospitals and insurance organizations increasingly use Aadhaar verification to validate patient identification and policyholder information. By having L1 scanners at hand, these organizations can more effectively attain faster and more accurate identification and reduce the forgery rate while improving service delivery.
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Banking Sector
One of the top banks in India used L1 RD fingerprint scanners at rural branches to speed up the AEPS transaction process. Before upgrading, most customers experienced transaction failures because of inadequate fingerprint recognition. With the migration to L1 devices, the bank experienced a 30% increase in the success rate of transactions, and customer satisfaction increased substantially.
Case Study 2: Government Welfare Programs
One state government tested L1 devices for pension payments to minimize fraud and the payment of funds only to legitimate recipients. The new scheme also minimized duplicate claims so that funds were paid correctly and efficiently.
Step-by-Step Migration Guide
Organizations can proceed to transition to L1 RD devices as seamlessly as possible by taking the following steps:
-
Evaluate Existing Infrastructure: Evaluate the number of existing L0 devices in use and determine whether one needs to upgrade to L1 scanners.
-
Acquire UIDAI-Approved L1 Scanners: Acquire new equipment that is UIDAI-certified and preferred standard.
-
Upgrade Software Infrastructure: Collaborate with IT personnel to install L1 support on current software infrastructure.
-
Train Staff and Users: Train staff and users to introduce them to new equipment and authentication protocols.
-
Monitor Performance: Monitor the performance of the new equipment continuously to authenticate more effectively with less failure.
Industry Response and Expert Opinions
Stakeholders in the biometric security and fintech sectors have welcomed the move to L1 RD fingerprint scanners with open arms. They comment that L1 devices are a significant step in enhancing the security and efficiency of Aadhaar-based authentication. Organizations are adopting the technology in force to stay in line with UIDAI's mandate and offer enhanced services to customers.
Future of Aadhaar-Based Authentication
With the advent of L1 RD fingerprint readers, Aadhaar authentication will be faster, more secure, and more reliable. Aadhaar-based services in the coming years hold the promise to be successful with fewer authentication failures, improved fraud protection, and an improved user experience, enhancing fraud detection and security of data as well.
Conclusion
Transition to L1 RD fingerprint scanners from L0 is a major leap in Aadhaar-based authentication technology. L1 devices offer enhanced accuracy, quicker processing, and stronger security, which will help services in the banking, government welfare programs, corporate management, and healthcare sectors. Organizations need to make sure they are well-equipped to switch to L1 devices so they can stay compliant and fully take advantage of the features these new scanners have to offer.
By embracing this shift, India is all the closer to an Aadhaar system that is more efficient, secure, and user-friendly, and ultimately better serving the experience of tens of millions of users who depend upon biometric authentication to access vital services.























