In the new digital age, keeping personal information safe is now more crucial than ever, especially in the condition of sensitive information such as biometric information. Biometric authentication systems that use unique physical attributes such as fingerprints or iris scans to identify people have been a common mode of securing internet transactions and access to services. In India, where Aadhaar-based authentication is common, biometric devices form the core in keeping user information secure.
Biometric devices are divided into various security levels, and among them are the L0 and L1 devices. The distinction between the two is quite clear, as both are indicative of varying security levels and compliances. L1 devices, being more secure with a greater degree of encryption, are taking a larger role to play, especially with the concentration on tighter security measures by UIDAI, which is the supervisory body of Aadhaar.
This blog will have a look at the very significant differences between L0 and L1 biometric devices, why it is necessary to shift to L1, and how specific devices such as Morpho MSO e3 L1, Mantra MFS110, Precision PB1000, and Startek Acsess FM220 u L1 are catering to these evolving needs.
What Are L0 and L1 Biometric Devices?
Biometric devices have been classified based on their ability to lock biometric data into different levels. L0 devices are the convenient option, handling data in the most primitive and insecure way. The devices store the biometric data directly on the host system such as a computer or mobile phone. While these tools offer a rudimentary sense of security, they do not feature complex encryption or any other higher level of security function. This makes them more vulnerable to data invasion and unauthorized access.
On the other hand, L1 devices are far more secure. They encrypt the biometric information inside the device, and hence they offer more protection. The encryption is done inside a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), thereby even if the host platform is compromised, data will remain protected. L1 devices also incorporate features such as anti-spoofing and live fingerprint detection, hence they are much more trustworthy for safe authentication.
Key Differences Between L0 and L1 Biometric Devices
Placing L0 and L1 devices side by side, there are various aspects in which they differ to make L1 devices a preferable choice for those organizations that would want security, compliance, and reliability as priority factors in the long term.
-
Security Level: The main difference between L0 and L1 devices is their security feature. Both L0 devices store and encrypt the biometric data in the host device and therefore are exposed to attacks from external factors. L1 devices encrypt data within the device and therefore if the host device becomes compromised, data will be safe. Anti-spoofing and live detection that identify attempts made for circumventing authentication are also provided with L1 devices.
-
Data Handling and Encryption: L0 devices are cryptography methods operated within the host device, and so they can easily be targeted for attacks. L1 devices make use of a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), which is substantially more secure than L0s and protects that sensitive biometric data never escapes to attackers' reach. L1 devices then become much more secure in selection for businesses and organizations caring most about the protection of their information.
-
Regulatory Compliance: L0 devices do not have the updated UIDAI specification to conduct Aadhaar authentication and therefore are non-compliant devices against guidelines designed for the safeguard of biometrics data. At the same time, L1 devices are highly compliant with the tight security demands put forth by UIDAI to help organizations availing of them maintain legal compliancy.
-
Authentication Speed and Accuracy: While L0 devices might be utilized effectively under low-risk applications, they take longer and are less secure with regards to authentication. L1 devices are meant to offer more rapid and accurate biometric comparison so that transaction times are sped up and instances of authentication error are reduced to the bare minimum. This is beneficial to users, especially within high-usage scenarios.
-
Cost: First of all, L0 devices are more affordable than L1 devices, and thus they are suitable for organizations with minimal budgets. Nevertheless, due to the fact that they are less equipped, periodic upgrades or replacements will be required in order to maintain compliance and security. L1 devices, while costly in the first instance, are durable and provide long-term benefits by way of cost-saving through the mitigation of the threat of data breach, errors, and compliance.
Why L1 Devices Are Becoming Essential
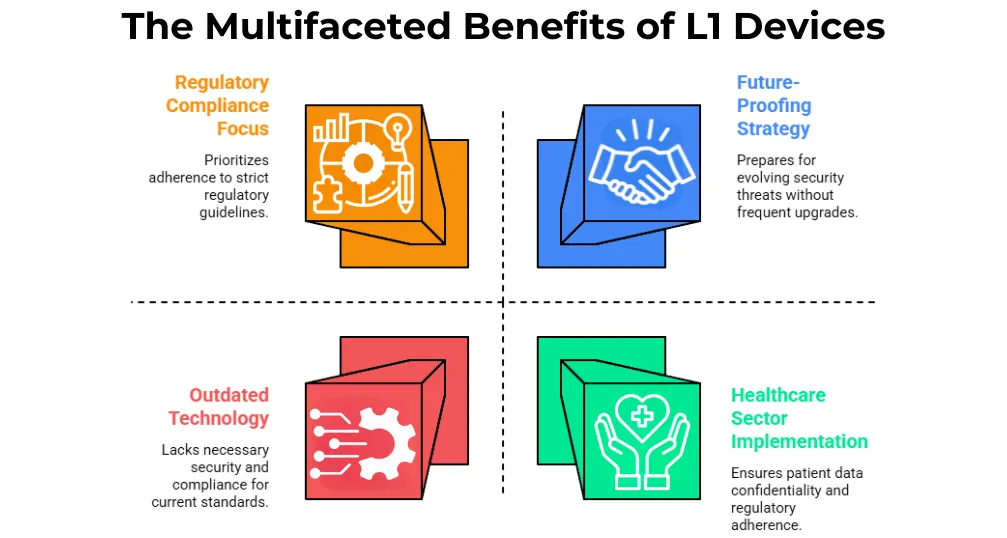
With threats to security getting more sophisticated by the day, L1 devices are progressively being the norm in biometric authentication systems, especially in risk-sensitive environments like healthcare, banking, and government services. The following are some reasons why there is increasing emphasis on L1 devices:
-
Improved Security: Apart from secure encryption, L1 devices offer more advanced security measures to ensure that biometric data is not accessed by unauthorized persons. In the healthcare sector, where confidentiality of patient medical data is of prime concern, this is particularly important.
-
Regulatory Compliance: UIDAI made Aadhaar-based authentication mandatory as strict guidelines, and L1 devices support all such guidelines. Since L0 devices are in the process of being phased out, it becomes important for organizations to use L1 devices so that they become legally compliant and avoid fines.
-
Future-Proof Investment: L1 devices are built to withstand future security threats and provide returns for decades. By contrast, L0 devices would need to be replaced each time regulations change and would be costly to replace in order to keep up with security standards.

Top L1 Biometric Devices in the Market
Some of the top biometric devices have been created in order to provide the security demands of L1 standards. Here are a few of the top choices:
Morpho MSO e3 L1 is an extremely well-respected biometric solution that is widely acclaimed for its excellent precision in fingerprint and iris scanning. Such a solution is greatly sought after in industries such as the healthcare industry, where safe and accurate identification of patients is extremely important. With advanced sensors and improved security features, the Morpho MSO e3 L1 securely stores biometric data encrypted inside the device, reducing the likelihood of data breaches and fraud. Its dependability and adaptability make it a best-fit solution for most healthcare providers in need of efficient patient identification systems.
The Mantra MFS110 is a fingerprint biometric terminal with quick and flawless authentication. It has fewer errors and less opportunity for impersonation, providing trouble-free and error-free registration and settlement of claims, particularly under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM). Mantra biometric terminals have gained acceptance for precision and speed and are a first choice for Aadhaar-based safe services in health and financial spaces as well.
The Precision PB1000 is also a biometric reader that has L1 security compliance. It has been found to be accurate in obtaining biometric data, and the Precision PB1000 reader was designed in particular to assist in meeting the demanding security needs of health care and other industries where proof of identity is critical. The reader has been designed for quick authentication, and that facilitates quick delivery of service, maintaining patient identification efficient and secure.
Startek Acsess FM220 u L1 is a fingerprint-based biometric reader that goes beyond secure identification and authentication. Rolled out on several healthcare systems using ABDM, Startek Acsess FM220 u L1 has been proven to be fraud-proof with accurate identification and providing access to Aadhaar-connected services securely. High security and performance make the device a goldmine for organizations seeking to secure sensitive biometric data.
Conclusion
L1 biometric products are a step in the future towards the security of sensitive and personal information in the era of constantly changing cyber attacks. The increasing demand for authentication of secured processes, especially in healthcare, finance, and public services industries, only goes to strengthen the necessity to embrace L1 standards further. The devices not only exist to meet but also aim to surpass changing security levels and regulatory needs, including that by UIDAI for Aadhaar-based authentication.
In addition to security, L1 device adoption has functional advantages. With the ability to support faster authentication rates, higher accuracy, and more resistance to fraudulent and spoof attacks, L1 devices provide a faster, more error-free user experience. This is most important where volume is high and fast and accurate identification are critical to operational success and customer satisfaction. Conversely, L0 devices can be prone to delays, mistakes, and weaknesses, ultimately tainting the user experience and exposing organizations to breaches and compliance issues.
L1 devices also have a definite long-term benefit in terms of costs. Although it is more to invest at first, the longer lifespan and conformity provided by L1 devices ensure less replacement and upgrading, and are therefore economical in the long run. Since there are heightened expectations of companies and organizations to safeguard sensitive biometric information, investing in L1 devices makes them compliant, competitive, and trusted by their customers.
With these benefits, the use of L1 biometric devices is not merely a security imperative—it is a strategic imperative that aligns within the greater objective of data protection, legislative adherence, and operational effectiveness. As firms embrace new levels of privacy and security, transitioning to L1 biometric devices is progress in the direction of the development of secure and future-proofed authentication infrastructure.























